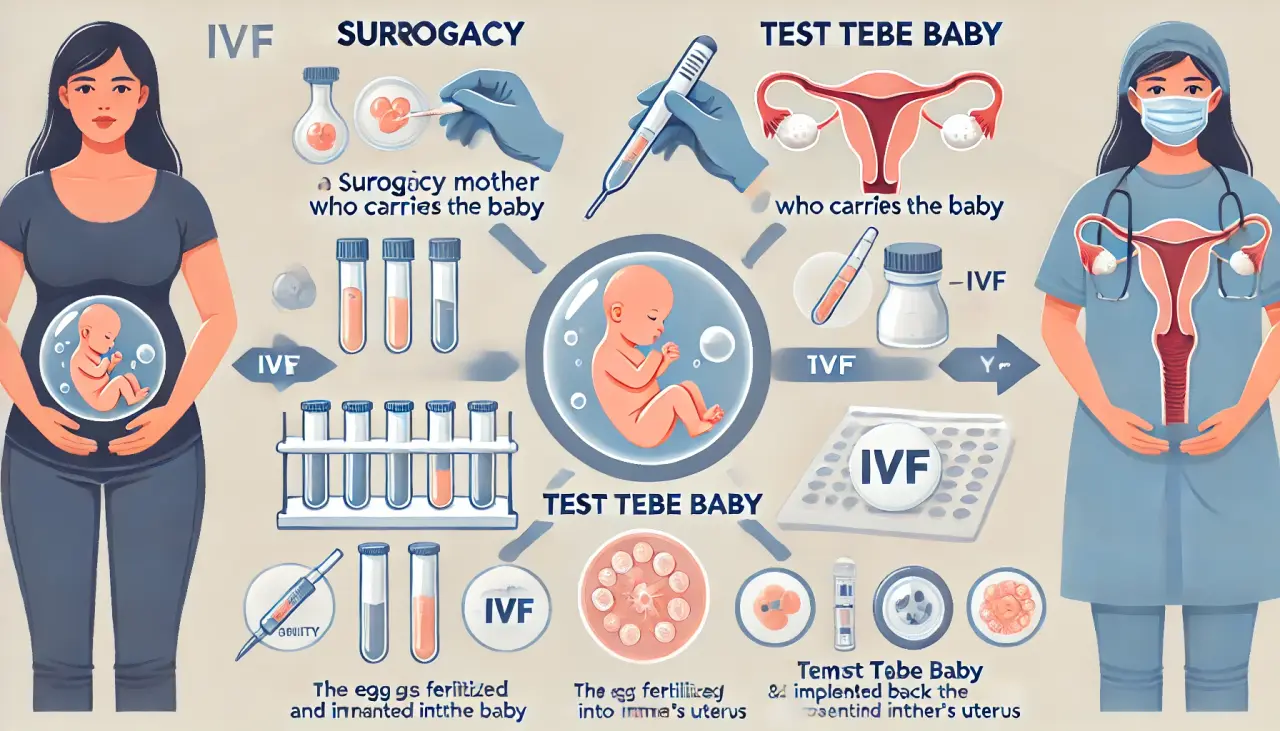
IVF Surrogacy vs. Test Tube Baby: Understanding the Complete Procedure and Key Differences
What is IVF Surrogacy and How Does It Work? IVF Surrogacy is a specialized form of infertility treatment where embryos created using the couple’s eggs and sperm are transferred to the uterus of a surrogate mother (gestational carrier). This method allows couples who are unable to bear a child themselves to achieve parenthood. If the pregnancy is successful, the couple can bring home a baby who is genetically related to both partners, which is the main advantage of this treatment option. IVF surrogacy is also a viable option for LGBT couples who may choose to use the eggs or sperm of one partner if neither can carry the pregnancy themselves.
Each party involved in IVF surrogacy undergoes an extensive screening procedure that includes fertility, medical, and genetic testing. Here is a step-by-step guide to the IVF surrogacy process:
- Synchronizing Menstrual Cycles: The intended (biological) mother, who is providing the eggs, and the gestational surrogate take medication to synchronize their menstrual cycles.
- Ovarian Stimulation: Once the cycles are synchronized, the intended mother begins ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval Procedure: When the eggs reach an adequate size, the intended mother undergoes an egg retrieval procedure.
- Fertilization with Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection: The collected eggs are fertilized with the partner’s (or donor’s) sperm in a specialized lab. Single sperm cells are injected directly into each egg through Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
- Embryo Culturing: The fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are cultured in the lab for 3 to 5 days.
- Preparing the Surrogate’s Uterus: After the ICSI procedure, the gestational surrogate starts taking hormone supplements to prepare her uterine lining for pregnancy.
- Embryo Monitoring and Grading: Embryos are regularly monitored and graded for quality during the grading cycle. Once the lab team determines that the embryos are ready, one or more are transferred to the surrogate’s uterus.
- Embryo Transfer: On day 3 or day 5, the embryos are transferred to the uterus of the surrogate mother.
- Pregnancy Test: Twelve days post-transfer, the surrogate takes a beta hCG test to determine if pregnancy has occurred.
- Prenatal Care: If pregnancy occurs, the surrogate begins receiving prenatal care.
- Birth and Parental Custody: After birth, the baby goes home with its biological parents.
IVF Surrogacy is becoming increasingly popular as many patients choose this treatment option as an alternative path to parenthood. To find out more about the process and costs of IVF surrogacy, visit our official website or schedule a free consultation.
Introduction to Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an infertility treatment for women who are unable to become pregnant or carry a baby to full-term. Understanding IVF surrogacy and its processes is crucial for couples considering this option. Often, some women experience the tragedy of repeated miscarriages after several pregnancies. Such couples can take the help of surrogacy to achieve their dream of parenthood. To find out more about surrogacy options, couples should contact a trustworthy surrogate agency.
Introduction to Test Tube Baby
A common misconception is that in vitro fertilization (IVF), often referred to as creating a “test tube baby,” is a purely scientific procedure with minimal involvement from the biological parents. Test Tube Baby treatment is perfect for couples who have not had success with other methods of assisted reproductive treatments. In vitro fertilization usually takes place in a shallow container called a petri dish, where eggs and sperm are combined to create embryos outside the body.
Difference Between Surrogacy and Test Tube Baby
There is a significant difference between surrogacy and test tube baby treatment processes:
- Surrogacy: Involves a surrogate mother—a woman (either a family member, friend, or an outsider)—who carries a baby in her womb and delivers the child for an infertile couple. To avoid any issues or disputes between the surrogate and the couple after the baby is born, proper legal steps should be taken before entering into an agreement.
- Test Tube Baby (IVF): Involves extracting ova and sperm from the biological parents and placing them in a fluid medium under proper conditions to allow fertilization. The fertilized egg, or embryo, is then implanted back into the intended mother’s uterus.
Steps in IVF
IVF Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproduction that has successfully helped couples who have difficulty conceiving a child without proper intervention. Here are the detailed steps involved:
- Ovarian Stimulation: The female partner is given specific medications to stimulate the ovaries, leading to the production of multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: These eggs are harvested through a surgical procedure once they have ripened.
- Sperm Collection: Sperms are then collected from the male partner and united with the eggs in the lab using Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
- Embryo Development: The embryos are cultured under optimal conditions in the laboratory for three to five days.
- Embryo Transfer: The most viable embryos are implanted back into the intended mother’s uterus. This is followed by a pregnancy test conducted after about a week. Pregnancy may occur in the first cycle itself, or more cycles may be needed depending on the average sixty percent success rate of IVF.
Conclusion
Success rates are significantly influenced by receiving treatment from the best medical professionals at reputable infertility clinics like the Indira IVF Centre. Experienced physicians achieve higher success rates, and often multiple embryos are transferred to increase the likelihood of pregnancy. However, this practice carries a higher risk of multiple pregnancies. Extensive testing and screening are conducted to ensure the best success for clients considering IVF surrogacy as an infertility treatment.