IVF Surrogacy: Understanding the Surrogacy Process and Treatment Options
What is IVF surrogacy and how does it work? IVF Surrogacy is a specialized form of infertility treatment where embryos created using the couple’s eggs and sperm are transferred to the uterus of a surrogate mother (gestational carrier). This method allows couples who are unable to bear a child themselves to achieve parenthood. If the pregnancy is successful, the couple can bring home a baby who is genetically related to both partners, which is the main advantage of this treatment option. IVF surrogacy is also a viable option for LGBT couples who may choose to use the eggs or sperm of one partner if neither can carry the pregnancy themselves.
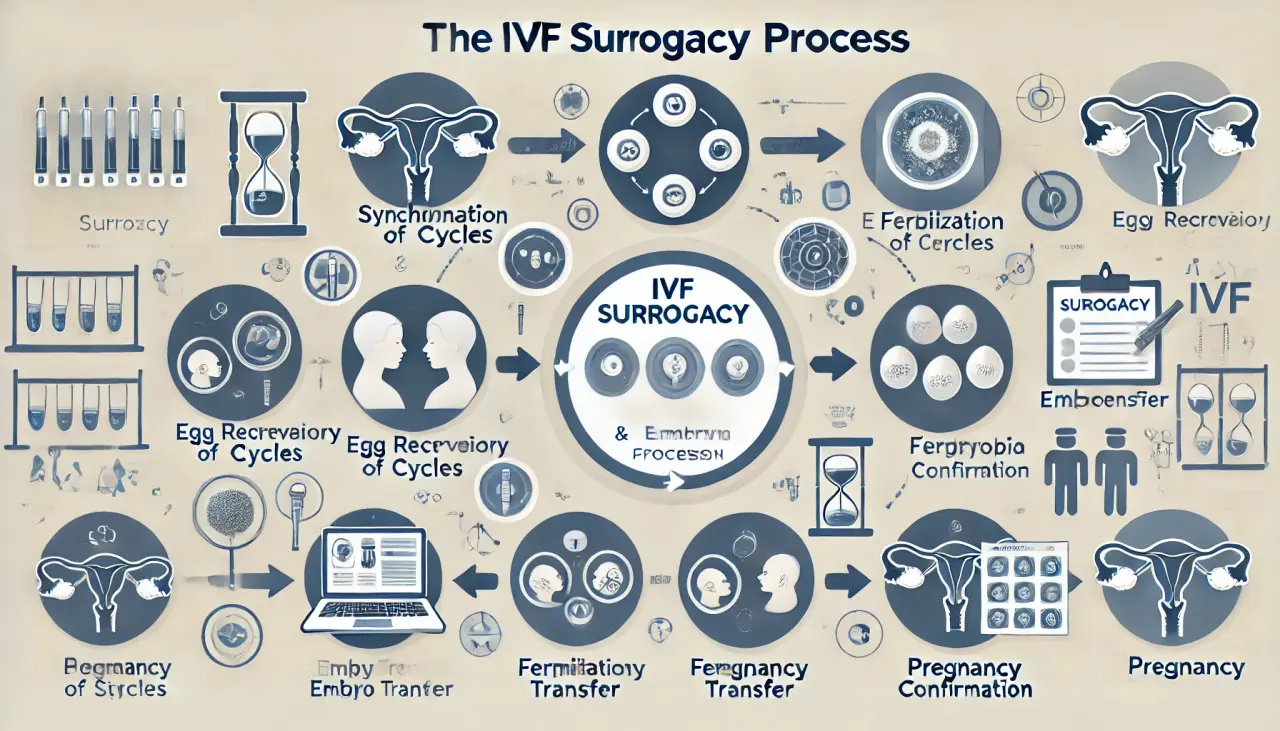
Each party involved in IVF surrogacy undergoes an extensive screening procedure that includes fertility, medical, and genetic testing. From here, the step-by-step guide to the IVF surrogacy process is as follows:
- Synchronizing Menstrual Cycles: The intended (biological) mother, who is providing the eggs, and the gestational surrogate take medication to synchronize their menstrual cycles.
- Ovarian Stimulation: Once the cycles are synchronized, the intended mother begins ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval Procedure: When the eggs reach an adequate size, the intended mother undergoes an egg retrieval procedure.
- Fertilization with ICSI: The collected eggs are fertilized with the partner’s (or donor’s) sperm in a specialized lab. Single sperm cells are injected directly into each egg through Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI).
- Embryo Culturing: The fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are cultured in the lab for 3 to 5 days.
- Preparing the Surrogate’s Uterus: After the ICSI procedure, the gestational surrogate starts taking hormone supplements to prepare her uterine lining for pregnancy.
- Embryo Monitoring and Grading: Embryos are regularly monitored and graded for quality during the grading cycle. Once the lab team determines that the embryos are ready, one or more are transferred to the surrogate’s uterus.
- Embryo Transfer: On day 3 or day 5, the embryos are transferred to the uterus of the surrogate mother.
- Pregnancy Test: Twelve days post-transfer, the surrogate takes a beta hCG test to determine if pregnancy has occurred.
- Prenatal Care: If pregnancy occurs, the surrogate begins receiving prenatal care.
- Birth and Parental Custody: After birth, the baby goes home with its biological parents.
IVF Surrogacy is becoming increasingly popular as many patients choose this treatment option as an alternative path to parenthood. To find out more about the process and costs of IVF Surrogacy, visit our official website or schedule a free consultation.